IoT sensors are driving a quiet but powerful revolution in how cities manage environmental challenges, especially air pollution. In a city like Jodhpur, known for its vibrant culture and dry desert climate, the growing burden of poor air quality is becoming impossible to ignore. Dust storms, increasing vehicular emissions, and industrial activity have made air pollution a year-round concern for both authorities and residents.
To tackle this issue head-on, the Jodhpur Municipal Corporation is turning to cutting-edge smart city solutions. By integrating IoT sensors into its urban infrastructure, the city is gaining the power to monitor, understand, and react to air pollution in real-time. This article dives deep into how this initiative is unfolding, what technologies are being used, the benefits for citizens, and how it fits into the broader vision of a healthier, more connected Jodhpur.
Understanding IoT Sensors and Their Role in Air Monitoring
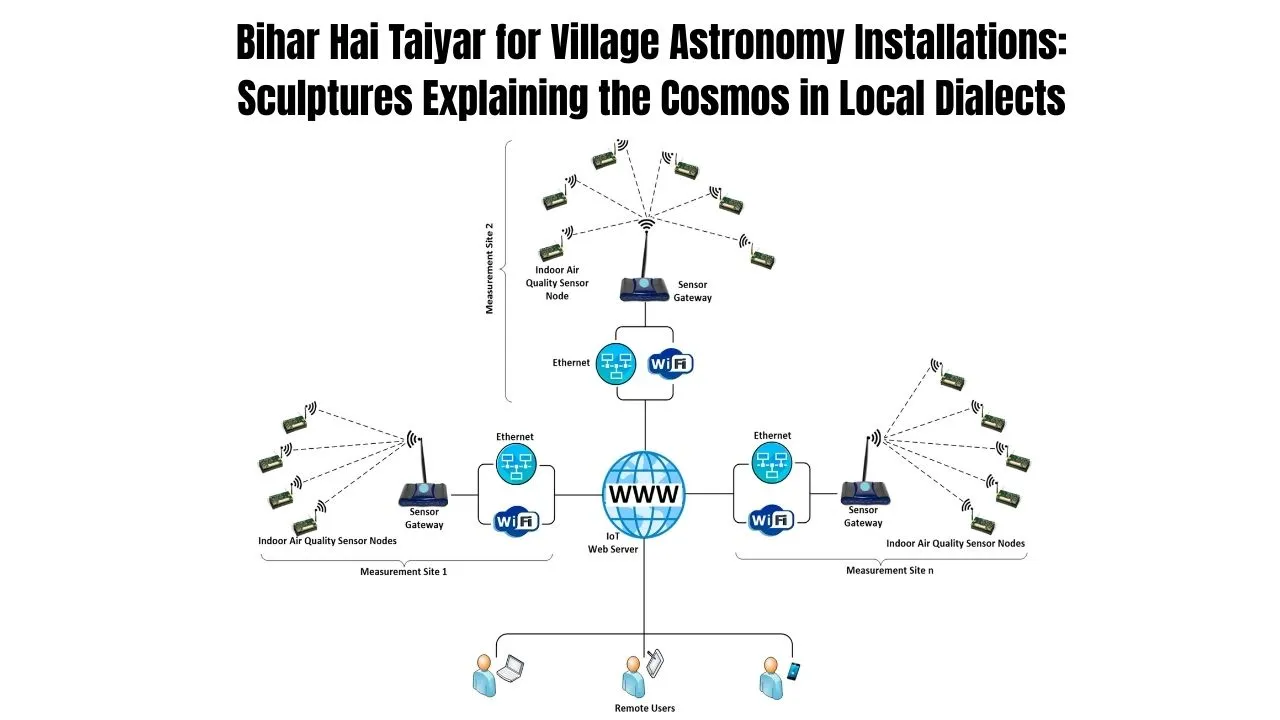
The use of IoT sensors in air quality monitoring involves deploying connected devices that constantly collect environmental data across different areas of a city. These sensors are capable of detecting airborne particles, gas concentrations, temperature, and humidity. The data is transmitted instantly to centralized platforms for analysis, allowing city planners and public health officials to make faster, more informed decisions. In Jodhpur’s case, this sensor network is becoming a foundation for both pollution control and urban health strategies, especially where traditional methods were slow or inefficient. By installing these devices at key locations, the Municipal Corporation is ensuring that real-time data becomes the backbone of its environmental monitoring efforts.
| Feature | Details |
| Sensor Types | PM2.5, PM10, CO2, NO2, temperature, humidity |
| Data Collection Frequency | Real-time (every few seconds to minutes) |
| Data Accessibility | Through public dashboards and mobile apps |
| Implementation Zones | Traffic-heavy areas, industrial regions, public spaces |
| Technology Partners | IoT and smart city tech firms |
| Citizen Benefits | Live updates, alerts, improved urban planning |
| Integration | Smart city dashboards, health alerts |
Why Jodhpur Needs Real-Time Air Quality Monitoring
Jodhpur’s unique geography and climate make it prone to dust and suspended particles. Combined with increasing traffic, construction activity, and industrial emissions, this leads to unsafe air quality levels throughout the year. Without timely information, the public and authorities have little ability to respond proactively.
Traditional monitoring methods using stationary labs or occasional testing are not enough. They often offer outdated readings, limited in scope. With real-time data from IoT sensors, city officials now have a complete view of what’s happening in the atmosphere at any moment. This immediate visibility is helping the city better plan, respond, and prevent air quality crises—particularly during seasonal dust storms or periods of high pollution.
How IoT Sensors Work in Air Quality Monitoring
Each IoT sensor is equipped with specialized instruments that detect various air pollutants, such as PM2.5, PM10, nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and carbon monoxide (CO). These pollutants are responsible for respiratory problems and other serious health risks. The sensors also measure weather variables, which are crucial in understanding how pollution spreads.
Once deployed, the sensors continuously send data to centralized servers via wireless communication. That data is then processed through cloud platforms and displayed on dashboards used by the Municipal Corporation. The system is also configured to push alerts when certain thresholds are breached. This technology makes it easier to identify high-risk areas and respond quickly by rerouting traffic, halting construction, or alerting healthcare facilities.
Role of Jodhpur Municipal Corporation in Implementation
The Jodhpur Municipal Corporation has taken a leadership role in adopting sensor technology to modernize its environmental policies. By mapping out pollution hotspots and carefully selecting sensor locations, they’ve created a connected network that spans across key parts of the city.
They’ve also ensured that this isn’t just a tech deployment exercise. City officials are using the data to shape real policies—like optimizing traffic flows, regulating construction during high-dust days, and promoting green zones in crowded neighborhoods. By linking real-time air monitoring with city planning, Jodhpur is moving closer to the goals of a true smart infrastructure model.
Key Benefits for Citizens
- Access to Real-Time Air Quality Data: Residents can check live updates on mobile apps, which helps them plan outdoor activities and avoid pollution peaks.
- Improved Public Health Responses: Hospitals and clinics can prepare for respiratory illness spikes by watching pollution trends.
- Smarter Environmental Decisions: Schools can reschedule outdoor events during bad air days, and employers can protect outdoor workers.
- Awareness and Engagement: The visibility of air quality data creates public awareness, encouraging eco-friendly habits among residents.
Major Areas Covered by IoT Sensors in Jodhpur
- High Traffic Zones
Sensors in congested areas monitor vehicular emissions in real-time. The data helps in adjusting traffic patterns, promoting carpooling, and encouraging the use of electric vehicles. - Industrial Zones
By monitoring emissions from factories, the Municipal Corporation ensures compliance with environmental standards. Action can be taken immediately if pollution levels exceed safe limits.
Data-Driven Decisions for Better Air Quality
The strength of this system lies in how it turns raw data into action. For instance, if the system detects rising pollution near a school, the city can instantly issue advisories or close playgrounds temporarily. On a larger scale, the collected data helps city planners rethink traffic routes, evaluate public transport needs, or expand green spaces where pollution is high.
Also, long-term environmental policies now have data backing. Instead of relying on guesswork, city authorities can use historical trends from IoT sensors to decide where to plant trees, where to move industries, or how to reduce dependency on fossil fuel vehicles. This blend of tech and policy is setting a precedent for smart city solutions across Rajasthan.
Challenges in Implementation
Every innovative project has hurdles. In Jodhpur, a few of the key challenges include:
- Ensuring continuous internet and power supply in sensor-equipped areas
- Calibration and maintenance of sensors to ensure accuracy
- Making data accessible and understandable for common citizens
- Training city staff to interpret and respond to data insights
Despite these, the Municipal Corporation has shown commitment to solving these issues by working with expert tech partners and investing in training programs.
Future Plans for Expanding the IoT Sensor Network
Looking ahead, Jodhpur plans to expand the sensor network to suburban and rural fringes, where pollution monitoring has often been neglected. There is also a vision to link this data with public healthcare systems, so that hospitals can prepare for pollution-related health emergencies in advance.
Another upcoming move is to introduce automated alert systems tied to weather forecasts. For example, if a dust storm is predicted, and pollution levels are already high, citizens will receive early warnings on their phones. These steps signal Jodhpur’s intent to become not just a smart city in name, but in function and resilience too.
FAQs
1. What pollutants do the IoT sensors in Jodhpur measure?
They detect PM2.5, PM10, CO2, NO2, and other airborne contaminants affecting health.
2. Can citizens view the air quality data?
Yes, real-time data is shared via dashboards and mobile applications accessible to the public.
3. How are sensor locations chosen?
The Municipal Corporation selects areas based on pollution levels, traffic, and public activity.
4. Do these sensors work during power cuts?
Most are equipped with backup batteries or solar power to ensure uninterrupted operation.
5. Is the data used for policymaking?
Yes, it supports city planning, emergency alerts, and environmental decisions.
Conclusion
The use of IoT sensors by the Jodhpur Municipal Corporation is a remarkable step toward combining smart technology with public health action. It’s not just about collecting data—it’s about using it meaningfully. By creating an intelligent, responsive, and inclusive air monitoring system, the city is showing how technology can genuinely improve lives.
As more cities in India consider smart upgrades, Jodhpur’s example offers a blueprint. Real-time insights, transparent communication, and decisive action—these are the pillars of a healthier urban future. Stay aware, stay informed, and explore your local air quality data. It’s more powerful than you think.